What is Dysphagia?
Dysphagia is the medical term for swallowing difficulties. Some people with dysphagia have problems swallowing certain foods or liquids while others can’t swallow at all. Rather than being a disease in its own right, it is often the consequence of an underlying condition1. Knowing how the swallowing process works is helpful in understanding dysphagia.
What is Dysphagia?
Dysphagia is the medical term for swallowing difficulties. Some people with dysphagia have problems swallowing certain foods or liquids while others can’t swallow at all. Rather than being a disease in its own right, it is often the consequence of an underlying condition1. Knowing how the swallowing process works is helpful in understanding dysphagia.
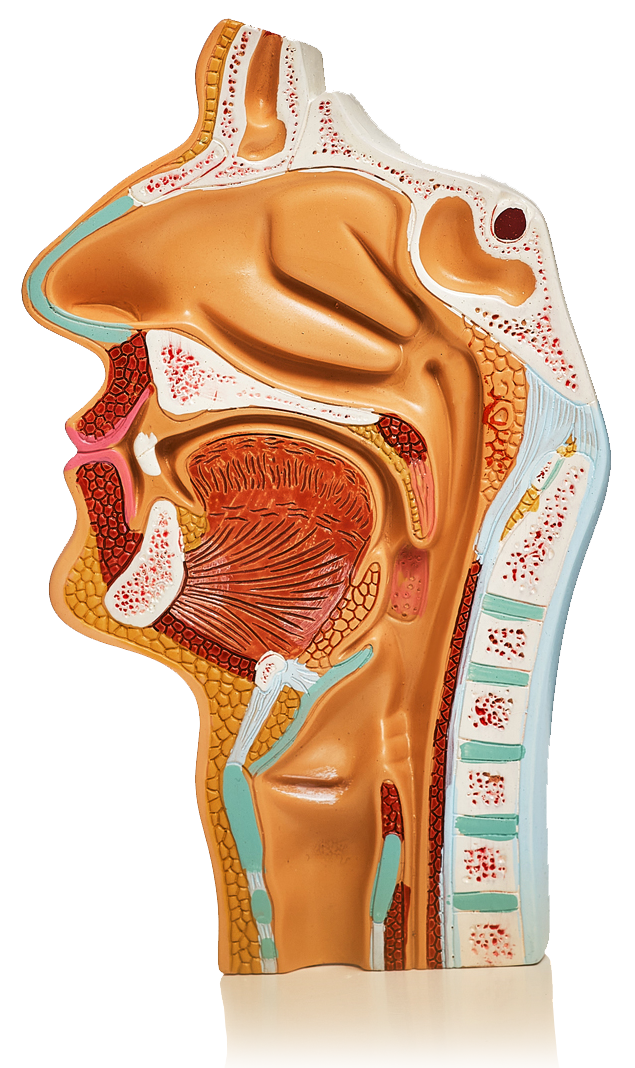
The Swallowing Process

A safe swallow
A safe swallow ensures that food, drink or medication is transferred from the mouth to the stomach, bypassing the airway and avoiding food or drink from entering the lungs (aspiration).
References
- NHS. Dysphagia (swallowing problems).
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/swallowing-problems-dysphagia/
Accessed: Dec 2024. - Physiology, Swallowing.
Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541071/
Accessed: Dec 2024. - Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals. The Normal Swallow.
Available at: https://www.nnuh.nhs.uk/departments/speech-and-language-therapy/swallowing/the-normal-swallow/
Accessed: Dec 2024. - Tracheostomy Education. Normal Swallowing.
Available at: https://www.tracheostomyeducation.com/normal-swallowing/
Accessed: Dec 2024.