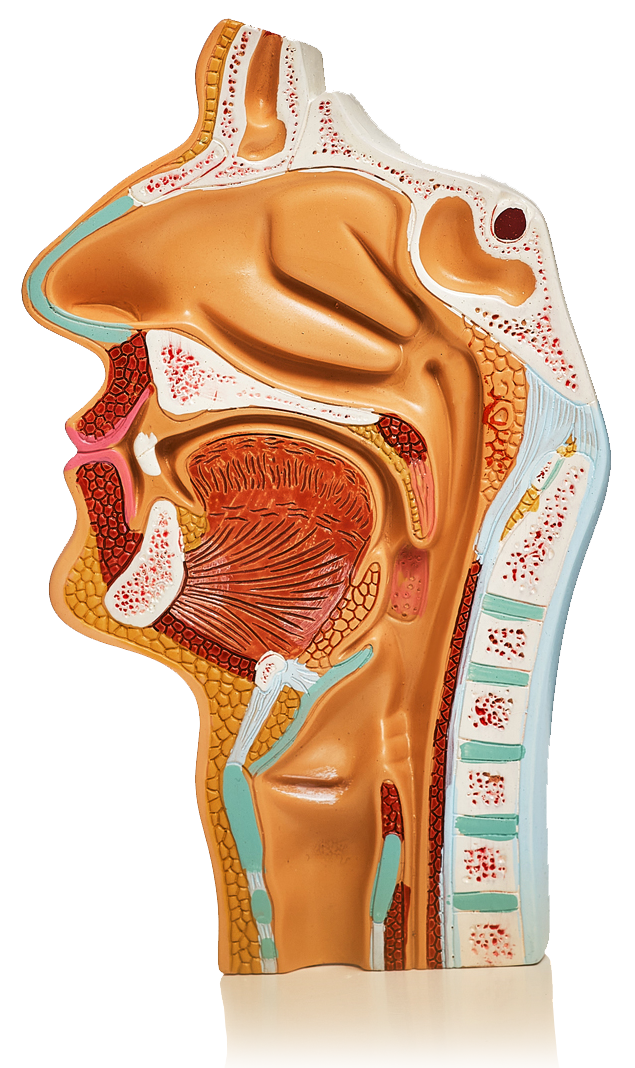
Glossary
The following definitions of medical and scientific terms may help in understanding what dysphagia is, what causes it and how it can be managed.
Achalasia
Failure of a ring of muscle (as a sphincter) to relax.
Acid Reflux
Gastro-oesophageal reflux causes both occasional heartburn and ongoing gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD).
Alzheimer’s Disease
A degenerative brain disease of unknown cause that is the most common form of dementia
Aspiration Pneumonia
Pneumonia resulting from inhalation of foreign bodies such as food particles.
Barium
A silver-white metallic element used as a contrast agent in medical imaging.
Beta Blockers
A class of drugs that decrease the rate and force of heart contractions and lower high blood pressure by blocking the activity of beta-receptors.
Botox (botulinum toxin)
A neurotoxin used in a purified form for therapeutic and cosmetic purposes.
Brain Tumour*
An abnormal growth of tissue in the brain which can be benign or malignant.
Cerebral Palsy
A disability resulting from damage to the brain before, during or shortly after birth and outwardly manifested by muscular incoordination and speech disturbances.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Pulmonary disease (such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis) that is characterised by chronic, typically irreversible airway obstruction resulting in a slowed rate of exhalation.
Cleft Palate
Congenital fissure in the roof of the mouth.
Congenital
Congenital conditions exist at or date from birth.
Dehydration
An abnormal depletion of body fluids.
Dementia
A usually progressive condition marked by the development of multiple cognitive deficits such as memory impairment, aphasia and the inability to plan and initiate complex behaviour.
Developmental Disabilities
Various conditions that usually become apparent during infancy or childhood and are marked by delayed development or functional limitations, especially in learning, language, communication, cognition, behaviour socialisation or mobility.
Diuretics
Diuretic drugs tend to increase the excretion of urine.
Dysphagia
Difficulty in swallowing.
Enteral feeding* (sometimes called tube feeding)
The delivery of nutrients and water through a gastrointestinal tube.
Enteric Coating*
A polymer barrier applied to oral medication that prevents its dissolution or disintegration in the gastric environment.
Fibreoptic Endoscope
A flexible instrument utilising fibre optics and used for examining inaccessible areas. Called a fiberscope in the USA.
Gastroenterology
A branch of medicine concerned with the structure, functions, diseases and pathology of the stomach and intestines.
Learning Disability
Any of various conditions that interfere with an individual’s ability to learn and so result in impaired functioning in language, reasoning or academic skills.
Malnutrition
Faulty nutrition due to inadequate or unbalanced intake of nutrients or their impaired assimilation or utilisation.
Manometry*
The recording of pressure of an inelastic liquid or gas used to diagnose motor disorders of the oesophagus and lower sphincter.
Modified Release
Designed to delay release of a drug in the body, usually until it passes through the stomach into the small intestine. Called delayed release in the USA.
Motility
The ability of the muscles of the digestive tract to undergo contraction, e.g. to propel food downward into the stomach.
Motor Neurone Disease
A rare progressive degenerative fatal disease affecting the motor neurons, usually beginning in middle age and characterised by increasing and spreading muscle weakness. Called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the USA.
Multiple Sclerosis
A demyelinating disease marked by patches of hardened tissue in the brain or the spinal cord and associated especially with partial or complete paralysis and jerking muscle tremor.
Nasoendoscopy
The examination of the nasal passages and pharynx by endoscope. Called nasopharyngoscopy in the USA.
Nasogastric (NG) feeding*
Feeding that consists of delivering liquid nutrients through a tube passing through the nose into the stomach.
Neurology
A branch of medicine concerned especially with the structure, function and diseases of the nervous system.
Nutritional Deficiency
An inadequate supply of essential nutrients (as vitamins and minerals) in the diet resulting in malnutrition and disease.
Oesophageal Dysphagia*
Dysphagia caused by an abnormality in the oesophagus.
Oesophagus
A muscular tube that leads from the mouth through the throat to the stomach.
Oral Cavity
The part of the mouth behind the gums and teeth that is bounded above by the hard and soft palates and below by the tongue and the mucus membrane connecting it with the inner part of the mandible.
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia*
Dysphagia caused by difficulty in initiating the swallowing process so that solids and liquids cannot move out of the mouth properly.
Parkinson’s Disease
A common progressive neurological disease chiefly of later life that is linked to decreased dopamine production in the brain and is marked especially by tremor of resting muscles, rigidity, slowness of movement, impaired balance and a shuffling gait.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube*
A tube placed through the abdominal wall with the aid of an endoscope into the stomach. Used for feeding patients unable to swallow food.
Peristalsis
Successive waves of involuntary contraction passing along the walls of a hollow muscular structure (like the oesophagus or intestine) and forcing the contents onward.
Pharynx
The muscular tubular passage of the vertebrate digestive and respiratory tracts extending from the back of the nasal cavity and mouth to the oesophagus.
Pneumonia
An acute disease that that is marked by inflammation of lung tissue and is characterised by fever, chills, cough, difficulty breathing, fatigue, chest pain and reduced lung expansion.
Proton pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
A group of drugs that are used to inhibit gastric acid secretion.
Radiotherapy
The treatment of disease with radiation (such as x-rays).
Speech & Language Therapy (SLT)
Therapeutic treatment of impairment and disorders of speech, voice, language, communication and swallowing. Called speech therapy in the USA.
Stroke
Sudden impairment or loss of consciousness, sensation and voluntary motion that is caused by rupture or obstruction (as by a clot) of a blood vessel supplying the brain and is accompanied by permanent damage to brain tissue.
Thrush
Oral thrush is a disease caused by a fungus (Candida albicans), occurs especially in infants and children and is marked by white patches in the oral cavity.
Tuberculosis
A highly variable communicable disease that affects especially the lungs but may spread to other areas such as the kidney or spinal column.
Scleroderma
A usually slowly progressive disease marked by the deposition of fibrous connective tissue in the skin and often in internal organs and structures.
Videofluoroscopy*
A videotaped dynamic x-ray of the functioning of an organ, especially in the gastrointestinal tract.
References
Available at:
https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical
Accessed 28 February 2022.
Available at:
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com
Accessed 28 February 2022.