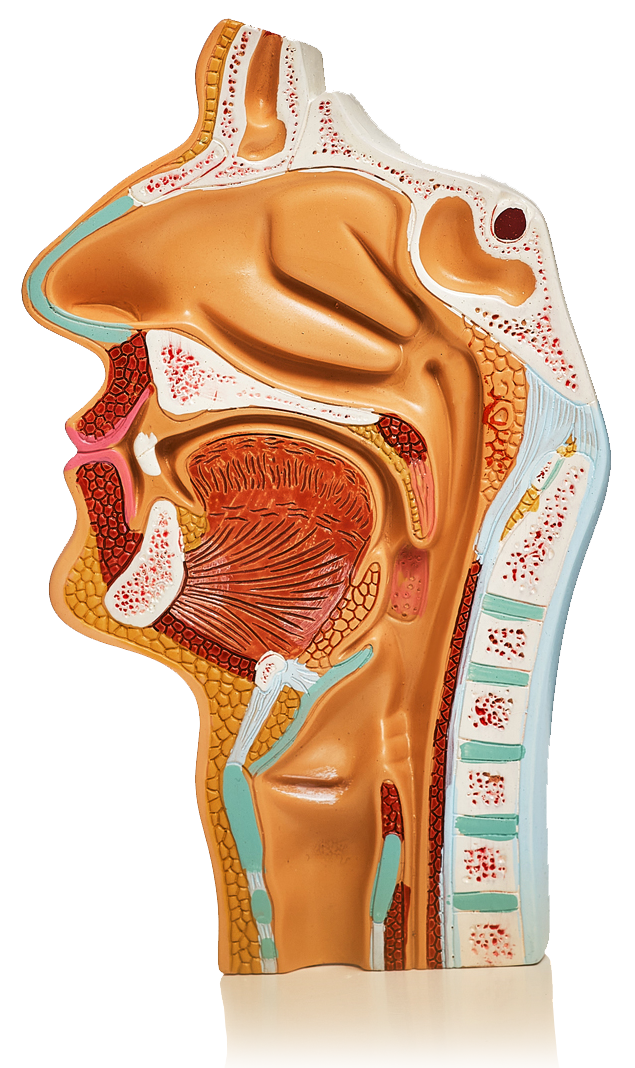
What causes it and who is most affected?
What causes it?1
There are two main types of dysphagia. One is due to problems in the mouth or throat (oropharyngeal dysphagia) and the other is due to problems in the gullet, the tube leading from the throat to the stomach (oesophageal dysphagia).
In some cases, dysphagia occurs for no obvious reason. However, it is typically caused by an underlying illness or condition.2 Causes include:1




Who is most affected?

Older People
An estimated 50-75% of care home residents have some difficulty swallowing4

Stroke Survivors
Dysphagia affects over 50% of survivors immediately after a stroke5

Dementia in care homes
68% of those with dementia in care homes show signs of dysphagia4
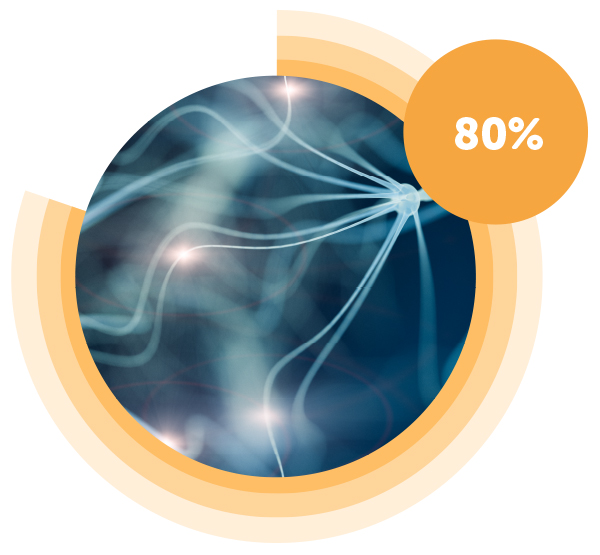

Motor Neurone Disease
As the disease progresses, dysphagia occurs in more than 80% of people living with it4

Cancer
Dysphagia occurs in over 50% of patients with head and neck cancer6

COPD
Around 27% of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease will experience dysphagia4
References
- NHS. Causes. Dysphagia (swallowing problems).
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/swallowing-problems-dysphagia/causes/
Accessed 28 February 2022. - NHS. Overview. Dysphagia (swallowing problems).
Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/swallowing-problems-dysphagia/
Accessed 28 February 2022. - Mayo Clinic. Dry Mouth.
Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dry-mouth/symptoms-causes/syc-20356048
Accessed 28 February 2022. - Holdoway A, Smith A. Malnutrition Pathway. Dysphagia.
Available at: https://www.malnutritionpathway.co.uk/dysphagia.pdf
Accessed 28 February 2022. - Gonzalez-Fernandez M, et al. Dysphagia after Stroke: an Overview. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep Sept 2013; 1(3): 187-196
- Garcia-Peris P, et al. Long-term prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients:
impact on quality of life. Clin Nutr. 2007 Dec;26(6):710-7.